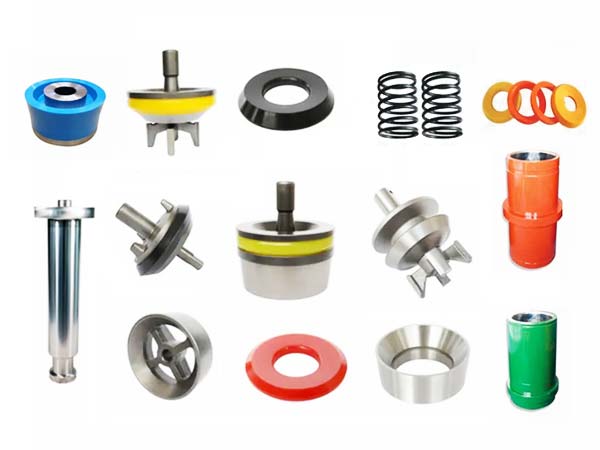

Published on: Feb 02, 2025
During oil and gas drilling, the mud pump is one of the core components of the drilling fluid circulation system. To ensure smooth circulation within the wellbore, the mud pump operates under high pressure and heavy loads for extended periods. Due to continuous friction, pressure impact, and corrosion, some components wear out and require regular replacement. These parts are known as mud pump expendables.

This article will introduce some common mud pump expendables we frequently help our clients source for oil and gas drilling projects and explain why they wear out over time.

Main Types of Mud Pump Expendables and Their Locations
Mud pump expendables can be categorized based on their location within the pump. Each component plays a specific role in the pump’s operation. Let’s take a look at the expendables found in the fluid end and power end of the mud pump.
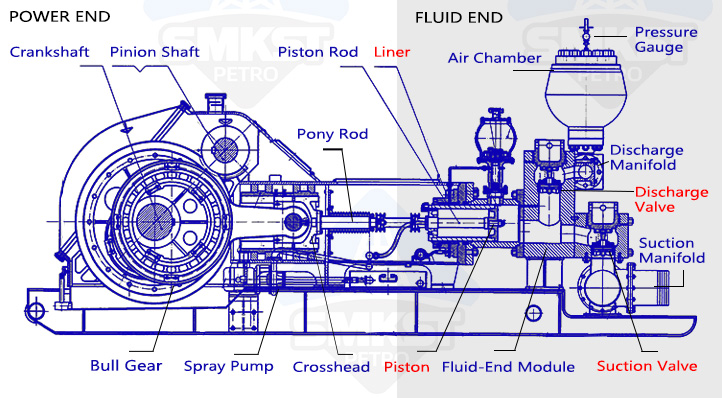
1.1 Fluid End Expendables
The fluid end is one of the most critical sections of the mud pump. It is responsible for the intake and discharge of drilling fluid and operates under extreme pressure, impact, and constant exposure to abrasive particles. Because of this, the components in the fluid end must have high wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and pressure tolerance.
Since the fluid end is directly exposed to high-pressure drilling fluid and experiences high-speed motion, its internal components are more prone to wear and failure than those in the power end. Below are the main mud pump fluid-end expendables:
- Liner: Installed on the inner wall of the pump cylinder, it provides wear resistance and protection. The piston moves back and forth at high speed inside the liner, leading to gradual wear over time.

Ceramic liners for mud pumps - Piston & Piston Rubber: The piston pushes the drilling fluid, while the piston rubber ensures a tight seal. Due to constant contact with high-pressure mud, the rubber material wears out and deteriorates.

Mud Pump Piston Assembly - Valve Body & Valve Seat: These components control the one-way flow of drilling fluid and withstand intense pressure impacts. Repeated opening and closing lead to fatigue and surface wear.

Mud pump valve - Seal Ring: Prevents mud leakage, but long-term use can lead to seal failure.

Mud pump liner gaskets and seals
1.2 Power End Expendables
The power end is the mechanical core of the mud pump. It converts mechanical energy to drive the reciprocating motion of the piston, ensuring the continuous high-pressure circulation of drilling fluid. Although the power end does not come into direct contact with drilling mud, it experiences significant mechanical stress and heavy loads. This leads to wear, fatigue, and potential failure of key components.
The main power end expendables include:
- Piston Rod: Connects the piston to the power end and undergoes constant tensile and compressive stress, which can lead to fatigue failure over time.
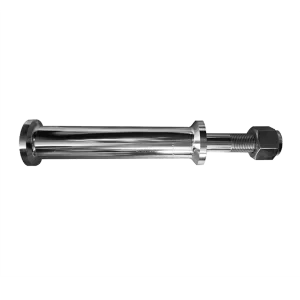
Mud pump piston rod - Crosshead: Ensures the stability of piston movement. If lubrication is insufficient, it can wear out quickly due to high loads.

Crosshead parts
2. Why Do Mud Pump Expendables Wear Out Easily?
You might wonder why these parts deteriorate so quickly. The primary reason is the harsh environment of oil and gas drilling. Here are the main factors contributing to expendable wear:
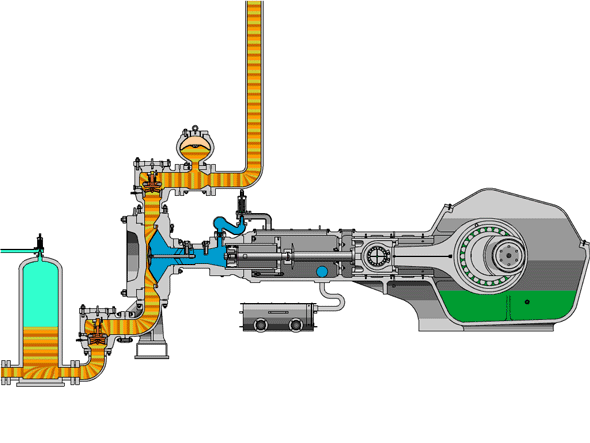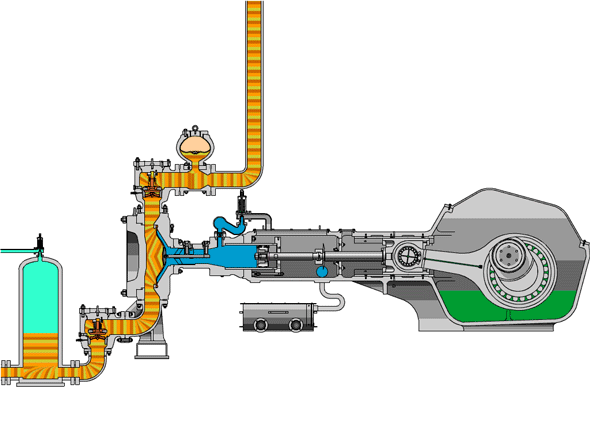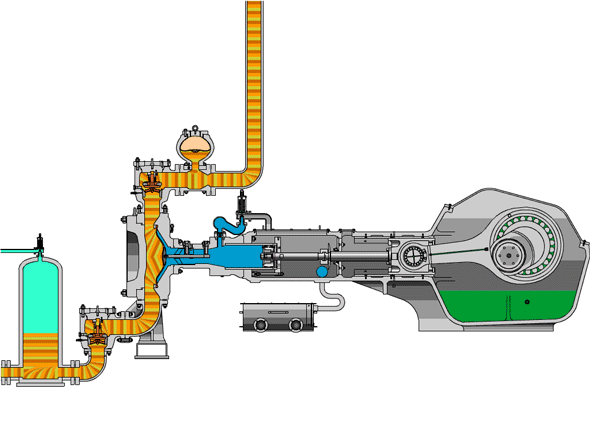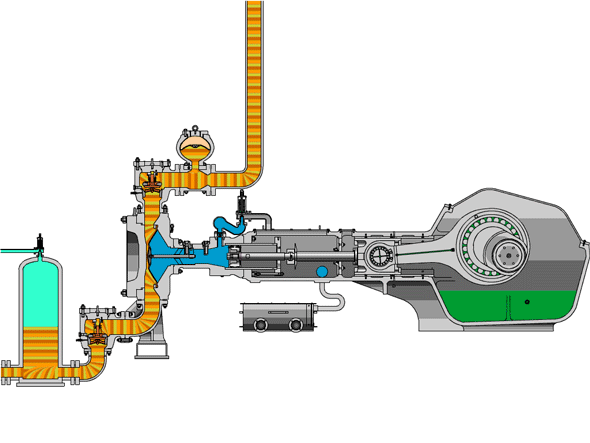
- High-Pressure Impact: The fluid end operates under extreme pressure, causing components like the valve body and liner to suffer surface fatigue and wear.
- High-Speed Reciprocating Motion: Parts such as the piston, piston rod, and liner are subject to constant friction, leading to gradual degradation.
- Abrasive Mud Particles: Drilling fluid often contains solid particles, which continuously erode the surface of components under high pressure. Larger sand and rock fragments can accelerate valve and piston damage.
- Chemical Corrosion: Drilling fluids may contain corrosive substances like salt water, hydrogen sulfide, and acidic chemicals, which accelerate the deterioration of metal and sealing components. This can result in pitting and structural failure.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Extreme temperatures can cause rubber seals and piston rubbers to harden or soften, reducing their lifespan. Continuous thermal expansion and contraction can also cause fatigue cracks in metal parts.
- Insufficient Lubrication: Some components, such as crosshead bearings, require regular lubrication. Poor lubrication or contamination can increase wear and lead to failure.
Conclusion
Mud pump expendables play a vital role in oil and gas drilling operations. Due to high pressure, high-speed friction, and corrosive conditions, these parts must be regularly replaced to maintain optimal performance.
As a professional supplier in the oil drilling industry, SMKST has extensive experience sourcing expendables for various international drilling projects. We provide high-quality mud pump expendables for a wide range of popular mud pump models and brands, ensuring safe and efficient drilling operations.
If you need to purchase mud pump expendables, feel free to contact us for a quote and technical support!
