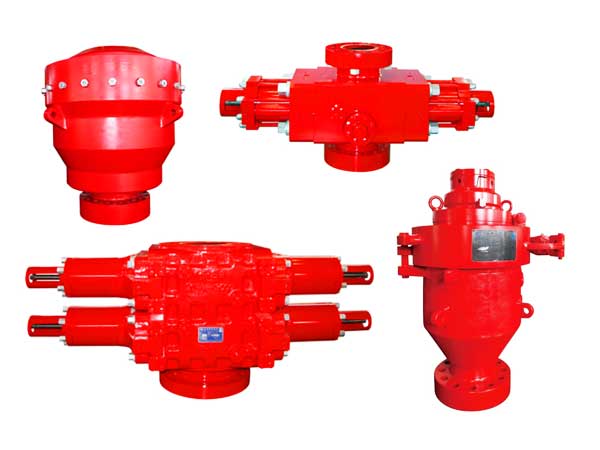

Published on: Aug 16, 2024
Ensuring safety during drilling operations is paramount in oil and gas exploration. The blowout preventer (BOP) is the core component of the well control system and serves as the last line of defense against abnormal downhole pressures and potential blowouts. This critical device not only provides essential protection during routine drilling but also reacts swiftly in emergencies, sealing the wellhead to prevent the uncontrolled release of high-pressure gases, oil, or other hazardous substances, thus safeguarding both personnel and equipment.

A thorough understanding of the different types and functions of BOPs is essential for making informed choices and operational decisions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the main types, features, and selection principles of BOPs, focusing on annular BOPs and ram BOPs. We will explore their classification, functional characteristics, and suitable applications, as well as offer practical advice on the selection, maintenance, and inspection of BOPs.
Whether you are a drilling engineer, a procurement specialist, or a student learning about drilling technology, this article offers valuable insights into this crucial safety device in drilling operations.
Part 1: The Three Main Types of Blowout Preventers
Blowout preventers are generally categorized into three types: annular BOPs, ram BOPs, and rotating BOPs. Each type has unique structural and functional characteristics and is typically used in combination within a BOP stack to ensure comprehensive well control. Below is a comparative overview of these three types:
| Feature | Annular BOP | Ram BOP | Rotating BOP |
| Sealing Element | Annular rubber packer | Flat ram | Rotating sealing elements (bearings and seals) |
| Sealing Mechanism | Packer contracts to the well center | Rams move towards the well center | Dynamic sealing through rotating elements |
| Adaptability | Accommodates various shapes and sizes of drill tools | Requires rams matched to specific sizes | Suitable for both rotating and non-rotating states |
| Versatility | High; one packer can adapt to multiple situations | Lower; different rams needed for different sizes | Medium; mainly used for specific operations |
| Sealing Method | Annular seal and full wellhead closure | Partial (around pipe) and full wellhead closure | Dynamic seal; allows drill string rotation |
| Special Functions | Stripping operations, soft shut-in | Shear drill tools, suspend drill string | Allows rotating under pressure and running in/out of the hole |
| Pressure Rating | Usually lower | Can reach very high levels | Medium, typically lower than ram BOPs |
| Sealing Reliability | Better under dynamic conditions | Better under static conditions | Best under rotating conditions |
| Operation Speed | Faster | Relatively slower | Continuous operation, no need for intervention |
| Maintenance Difficulty | Simpler; mainly replacing packers | More complex; requires changing various rams | Complex; requires regular bearing system maintenance |
| Service Life | Shorter, due to packer wear | Longer; rams are replaceable | Medium; affected by bearings and seals |
| Cost | Relatively low | Relatively high | High, especially in maintenance |
| Common Application Position | Top of the BOP stack | Middle to lower part of the BOP stack | Top of the BOP stack or used alone |
| Number in BOP Stack | Usually 1 | Usually 2 or more | Typically 0-1, depending on need |
| Main Application Scenarios | Routine drilling, emergency shut-in | Routine drilling, precise control, emergency handling | Pressurized rotating drilling, coiled tubing operations |
This table summarizes the key differences between the three main types of BOPs. Each type also has multiple models and variations. Let’s delve deeper into each primary classification.
Part 2: Annular BOPs and Their Classifications
Annular BOPs use an annular rubber packer as the sealing element, which can accommodate various shapes of drill tools and equipment. These BOPs are primarily used to seal the annular space between the drill string and the wellhead, fully seal the wellhead when the well is empty, and provide sealing capabilities during special operations. Annular BOPs can also be used for stripping operations and soft shut-ins.
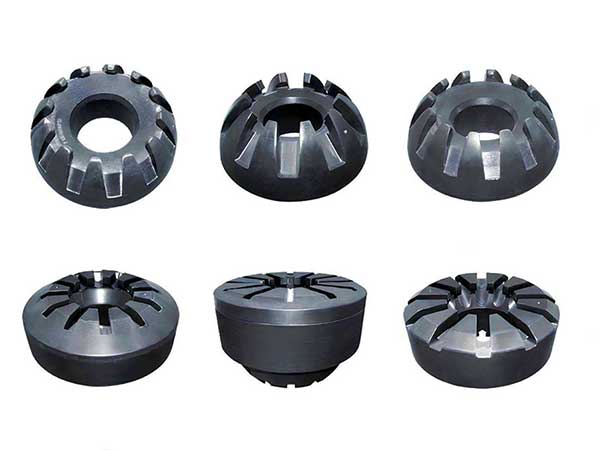

Annular BOPs can be categorized based on the shape of the packer, with conical and spherical packers being the most common.
| Type | Packer Shape | Sealing Method | Characteristics | Application Scenarios |
| Conical | Conical | Compressed from top to bottom | Reduces wear | Routine drilling operations |
| Spherical | Spherical | Squeezes towards the well center | Provides greater sealing force | High-pressure wells |
| Cylindrical | Cylindrical | Radial contraction | – | Large diameter wells or frequent tripping |
Each type of annular BOP has specific application scenarios. For instance, conical BOPs are commonly used in onshore drilling, while spherical BOPs are more frequently employed on offshore drilling platforms. Selection should consider factors such as well depth, pressure, and temperature.
Part 3: Ram BOPs and Their Classifications
Ram BOPs use flat rams as the sealing element, and different types of rams can be selected based on operational needs. The primary functions of ram BOPs include sealing the annular space of the wellhead, fully sealing the wellhead, shearing drill tools inside the well, suspending the drill string, side outlet throttling, pressure relief, and long-term well shut-in. Ram BOPs offer significant flexibility in managing complex downhole conditions.
Ram BOPs can be classified based on the following criteria:
| Classification Criteria | Type | Characteristics | Application Scenarios |
| Number of Rams | Single Ram | Simple structure | Low-pressure wells or as a backup |
| Double Ram | Most common; can install two different rams | Increased operational flexibility | |
| Triple Ram | It provides more sealing options | Complex well conditions or high-risk operations | |
| Ram Function | Full-Bore Ram | Fully seals the wellhead | Empty well situations |
| Pipe Ram | Seals around specific sizes of drill tools | The most commonly used type | |
| Shear Ram | Can shear drill tools and seal the wellhead | Emergency situations | |
| Variable-Bore Ram | Adapts to different drill string diameters | Increased flexibility | |
| Locking Method | Manual Lock | – | Low-pressure wells or as a backup system |
| Hydraulic Lock | Faster response | High-pressure wells and automated rigs | |
| Side Door Operation Method | Rotary Side Door | Easier maintenance and ram replacement; more complex operation | – |
| Linear Motion Side Door | Quicker operation | Frequent ram changes |
In practical applications, the selection of ram BOPs should consider factors such as well depth, pressure, temperature, and drill tool specifications, as well as specific operational needs and safety standards. Different types of rams can be combined to handle various well control situations.
Part 4: Rotating BOPs and Their Classifications
Rotating BOPs use rotating sealing elements (usually including bearings and seals) to maintain wellhead sealing while the drill string is rotating. These BOPs allow pressurized rotation and tripping, providing continuous sealing protection under dynamic drilling conditions. Rotating BOPs are particularly important in specialized drilling operations, such as pressurized drilling and coiled tubing operations.

Rotating BOPs can be classified based on the following criteria:
| Classification Criteria | Type | Characteristics | Application Scenarios |
| Sealing Element Design | Single Sealing Element | Simple structure | Low-pressure wells or short-term use |
| Double Sealing Element | Provides double protection | Medium to high-pressure wells or long-term use | |
| Multi-Sealing Element | High sealing reliability | High-pressure wells or harsh environments | |
| Bearing System | Ball Bearings | Low friction; suitable for high speed | High-speed rotating operations |
| Roller Bearings | High load-bearing capacity | Heavy load conditions | |
| Composite Bearings | Good overall performance | Complex working conditions | |
| Cooling System | Water-Cooled | Effective heat dissipation | High-temperature wells |
| Oil-Cooled | Good lubrication | Regular wells | |
| Air-Cooled | Simple structure | Low-temperature wells | |
| Pressure Rating | Low Pressure | Lower cost | Wells below 2,000 psi |
| Medium Pressure | Widely used | Wells between 2,000 and 5,000 psi | |
| High Pressure | Excellent sealing performance | Wells above 5,000 psi | |
| Drive Method | Passive | Simple structure; relies on drill string rotation | Regular rotating drilling |
| Active | Independent drive system | Situations requiring continuous sealing |
Part 5: Selection and Application of Blowout Preventers
Choosing the right blowout preventer is crucial for ensuring safe drilling operations. The selection process must consider factors such as well depth, expected pressure, wellhead size, drill tool specifications, environmental conditions, and regulatory requirements. Well depth and pressure determine the required pressure rating of the BOP, while wellhead size and drill tool specifications influence the selection of BOP size and ram configuration. Additionally, environmental factors like temperature range and potential corrosive media should be considered when selecting appropriate materials and designs.
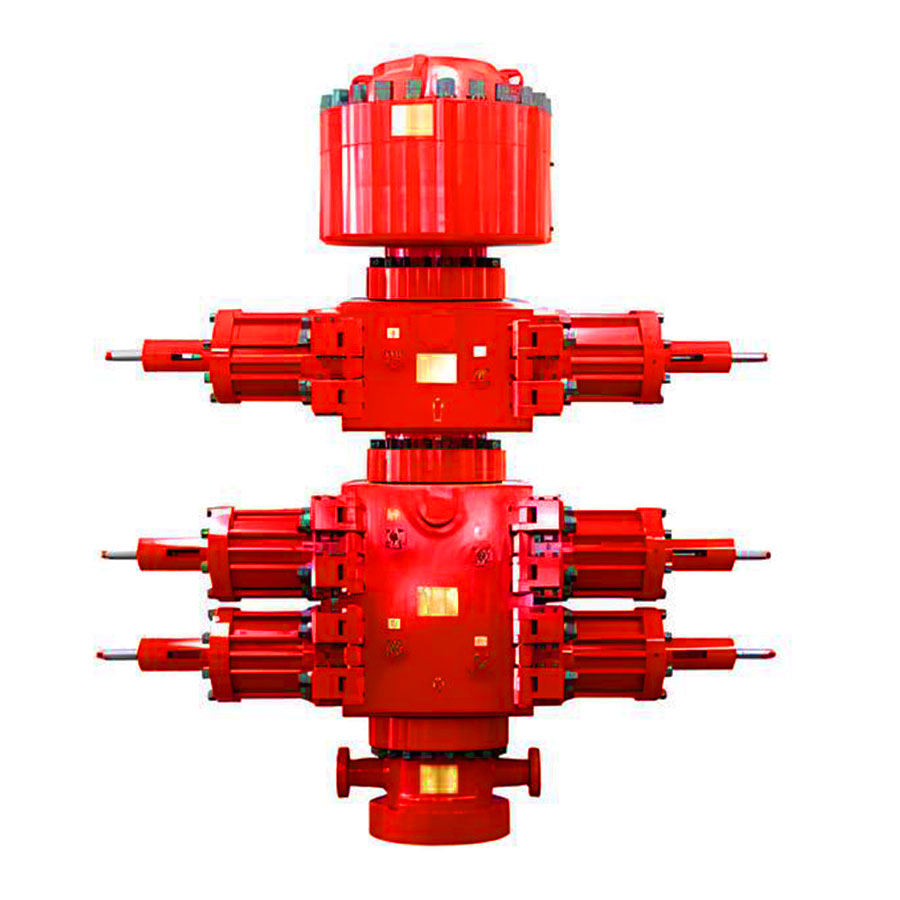

In practice, a standard BOP stack usually includes at least one annular BOP and two ram BOPs, with specific configurations varying based on project requirements. The type of rams should be adjusted according to different stages of the drilling plan. Regular testing, maintenance, and operator training are also critical for ensuring the effective operation of the BOP.
The selection and use of BOPs should be coordinated with other well-control equipment to form a complete well-control system. Consulting experienced engineers or BOP suppliers is recommended to ensure the most suitable BOP configuration is chosen for the specific drilling project. It’s important to note that BOPs are only part of the well control system, and their effectiveness depends on the design and operation of the entire system.
Conclusion
Blowout preventers play an irreplaceable role in the well control system, ensuring the safety of drilling operations. By thoroughly understanding the classifications, functions, and selection principles of annular and ram BOPs, we can better address the challenges that arise during drilling. However, selecting the right BOP is not enough; proper operation, regular maintenance, and comprehensive training are also necessary to fully realize the BOP’s capabilities. In the increasingly complex drilling environment, continuous attention to BOP technology and optimization of its application will provide strong guarantees for the safety and efficiency of drilling operations.
